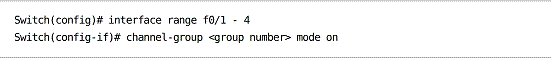EtherChannel Load Balancing
EtherChannel distributes load across multiple physical links by examining between one and three low order bits of an arbitrary address. XOR is used when multiple addresses are examined.
Address types eligible for examination:
Source and destination MAC – src-mac (default for L2 channels), dst-mac, or src-dst-mac
Source and destination IP – src-ip, dst-ip, or src-dst-ip (default for L3 channels)
Source and destination L4 port – src-port, dst-port, or src-dst-port (Catalyst 6500/4500 only)
Port channel load balancing is configured globally:
EtherChannel Negotiation
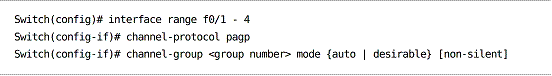
Port Aggregation Protocol (PAgP)
PAgP is Cisco proprietary.
Port channels are configured as desirable (active) or auto (passive).
Addition of the non-silent parameter will ensure the etherchannel will not be formed without receiving PAgP packets from the neighbor.
Configuring PAgP:
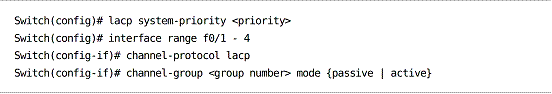
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP)
LACP is defined in IEEE 802.3ad.
The switch with the lowest priority designates which interfaces participate in the etherchannel.
Interfaces are configured as active or passive.
lacp port-priority <priority> is used to assign an LACP priority to individual ports.
Lower-priority interfaces beyond the eight-port limit for a single channel will be designated as standby interfaces should one of the higher-priority links fail.
Configuring LACP:
Static
EtherChannel interfaces can be set to on, forming a permanent etherchannel with no autonegotiation protocol (neither PAgP or LACP is used).
Troubleshooting
show etherchannel summary
show etherchannel port
show etherchannel load-balance
show {pagp | lacp} neighbor